http://www.sqlhub.com
Note: Microsoft Books online is a default reference of all articles but examples and explanations prepared by Ritesh Shah, founder of http://www.SQLHub.com
 Tuesday, June 21, 2011 |
Tuesday, June 21, 2011 |  Posted by
Ritesh Shah
Posted by
Ritesh Shah
 Monday, June 20, 2011 |
Monday, June 20, 2011 |  Posted by
Ritesh Shah
Posted by
Ritesh Shah
 Wednesday, June 15, 2011 |
Wednesday, June 15, 2011 |  Posted by
Ritesh Shah
Posted by
Ritesh Shah
 0
comments
0
comments
 Labels:
clustered index,
index,
Microsoft,
Ritesh Shah,
sql server 2005
Labels:
clustered index,
index,
Microsoft,
Ritesh Shah,
sql server 2005
 Thursday, May 7, 2009 |
Thursday, May 7, 2009 |  Posted by
Ritesh Shah
Posted by
Ritesh Shah
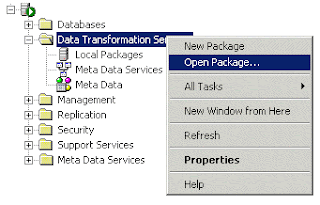
But you will not be able to see “Data Transformation Service” command in SSMS directly. Isn’t it there? Answer is, it is there but at other location.
Expand the Management object.
Open the Legacy object.
Right click on Data Transformation Services.
Click on "Open Package File"
Have a look at screen capture:

However, you can open old .DTS packages in SSMS but it is better to upgrade it to .DTSX package. There is one nice article at simple-talk.com. Have a look.
http://www.simple-talk.com
Reference: Ritesh Shah
http://www.sqlhub.com
Note: Microsoft Books online is a default reference of all articles but examples and explanations prepared by Ritesh Shah, founder of http://www.SQLHub.com
 0
comments
0
comments
 Labels:
.DTS,
.DTSX,
DTS,
Microsoft,
Ritesh Shah,
sql server 2005,
SSIS,
T-sql
Labels:
.DTS,
.DTSX,
DTS,
Microsoft,
Ritesh Shah,
sql server 2005,
SSIS,
T-sql
 Wednesday, April 1, 2009 |
Wednesday, April 1, 2009 |  Posted by
Ritesh Shah
Posted by
Ritesh Shah
If you are SQL Server geek, you must be aware with Stored Procedure. While question comes to implement stored procedure in front end language, many developers makes mistake or feel confusion as per my recent observation so I am tempted to write one article which can show how to handle stored procedure in C# when it return some value and when it return some record sets.
--CREATE TABLE
CREATE TABLE empDemo
(
ID INT NOT NULL,
NAME VARCHAR(50)
)
GO
--INSERT DATA
INSERT INTO empDemo
SELECT 1,'Ritesh' UNION ALL
SELECT 2,'Rajan'
--create SP which will return list of employee
--NOTE: this is just basic SP, you can create
--your own for your custom need.
CREATE PROC ListEmp (@id INT)
AS
BEGIN
SELECT * FROM empDemo WHERE ID=@id
END
--check SP whether it works.
EXEC ListEmp 2
Now, we will see C# code (in asp.net code behind) to return the list of employee:
protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//create connection string and assign it to SqlConnection object
string strConn = "Data Source=.;Initial Catalog=AdventureWorks;Persist Security Info=True;User ID=sa;Password=sa";
System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection conn = new System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection(strConn);
conn.Open();
//setup SqlCommand and assign SP name along with input parameter variable name and value
System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand command = new System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand();
command.CommandType = System.Data.CommandType.StoredProcedure;
command.Connection = conn;
command.CommandText = "ListEmp";
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("@id", "2");
//create one data adapter which will execute the command and fill the data into data set
System.Data.SqlClient.SqlDataAdapter recordAdp = new System.Data.SqlClient.SqlDataAdapter();
recordAdp.SelectCommand = command;
System.Data.DataSet recordSet = new System.Data.DataSet();
recordAdp.Fill(recordSet);
command.Dispose();
conn.Close();
//bind gridview1 with our dataset
GridView1.DataSource = recordSet.Tables[0].DefaultView;
GridView1.DataBind();
}
This seems basic but really useful for newbie, now what if we have some other DML command and we want to return value from SP and handle it in our C# ASP.NET.
--create SP to insert record and retun value
--we will handle return value in C# code behind
CREATE PROC InsertEmp(@ID INT, @Name VARCHAR(20))
AS
BEGIN
BEGIN TRY
INSERT INTO empDemo(ID,Name) VALUES(@ID,@Name)
return 1
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
return 0
END CATCH
END
--check SP works or not
EXEC InsertEmp 3,'Alka'
Now let us move to ASP.NET C# code behind.
protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//create connection string and assign it to SqlConnection object
string strConn = "Data Source=.;Initial Catalog=AdventureWorks;Persist Security Info=True;User ID=sa;Password=sa";
System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection conn = new System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection(strConn);
conn.Open();
//setup SqlCommand and assign SP name along with input parameter variable name and value
System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand command = new System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand();
command.CommandType = System.Data.CommandType.StoredProcedure;
command.Connection = conn;
command.CommandText = "InsertEmp";
command.Parameters.Add("@ReturnValue",System.Data.SqlDbType.Int);
command.Parameters["@ReturnValue"].Direction = System.Data.ParameterDirection.ReturnValue;
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("@id", "4");
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Name", "Bihag");
command.ExecuteScalar();
int i = Convert.ToInt32(command.Parameters["@ReturnValue"].Value);
if (i == 1)
{
Response.Write("Successfull!!!!");
}
else
{
Response.Write("Not Successfull!!!!");
}
}
Hope you have enjoyed it!!!!
Reference: Ritesh Shah
http://www.sqlhub.com
Note: Microsoft Books online is a default reference of all articles but examples and explanations prepared by Ritesh Shah, founder of http://www.SQLHub.com
 Monday, March 23, 2009 |
Monday, March 23, 2009 |  Posted by
Ritesh Shah
Posted by
Ritesh Shah
I have written many articles on differences and comparison on various topic of Microsoft SQL Server. Here is one more difference between Stored Procedure and User Define Function. Many times I have seen new developer in confusion about usage of functions so after finishing the series of articles in stored procedures and user define functions I thought to write one article for these differences.
Actually before Microsoft SQL Server 2000, there was no concept of UDFs and it has first been revealed in Microsoft SQL Server 2000 to wrap up your complex T-SQL logic but initially people were not started adopt it but I guess they have started focusing in it with Microsoft SQL Server 2005 when UDFs comes up with new features like table valued function and CLR function implementation. Now, the situation is, UDFs become one powerful tool in SQL Server kit.
The main difference I feel between SPs and UDFs is usage in SELECT. One can use UDFs anywhere in JOIN, FROM, WHERE and HAVING clause whereas SPs are not that much flexible.
UDFs are simple to invoke in any T-SQL statement then SPs.
Some DML statements like INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE are not permissible in UDFs whereas you can use it in SPs.
You can not call non-deterministic function of SQL Server inside the UDFs whereas you can call them in SPs. For example GETDATE() function, it is non-deterministic and can’t be called within UDFs.
Stored Procedure can call function but function can't call stored procedure.
User defined function can have only input parameter whereas SPs can have input as well as output parameter.
You can use Try...Catch in SPs whereas UDF can't support it.
If you are more interested to learn about SPs and UDFs than you can sear http://www.sqlhub.com for more details as I wrote dozens of article on this topic with so many real life examples.
Reference: Ritesh Shah
http://www.sqlhub.com
Note: Microsoft Books online is a default reference of all articles but examples and explanations prepared by Ritesh Shah, founder of http://www.SQLHub.com
 Friday, March 20, 2009 |
Friday, March 20, 2009 |  Posted by
Ritesh Shah
Posted by
Ritesh Shah
This is continuous topic of CURSOR. You can refer my past article on cursor at
http://ritesh-a-shah.blogspot.com/2009/03/what-is-cursor-definition-of-cursor-in.html
http://ritesh-a-shah.blogspot.com/2009/03/forwardonly-and-fastforward-cursor.html
http://ritesh-a-shah.blogspot.com/2009/03/dynamic-cross-tab-query-with-cursor-in.html
I gave definition of CURSOR and explained different type of CURSOR in my first article given above. Second article was for FORWARD_ONLY cursor and third one was for dynamic cross tab query with FAST_FORWARD cursor. Now this article will show you example of dynamic cursor which can move forward and backward as well. It will get fresh record set with every FETCH statement so that while fetching the record, we will be able to get fresh modified record by another user for our SELECT statement in SQL Server 2005.
Let us see it practically.
--create one table for demo
use adventureworks
CREATE TABLE emps
(
Name VARCHAR(50),
Dept VARCHAR(10),
Company VARCHAR(15)
)
--INSERT records
INSERT INTO emps
SELECT 'Ritesh','MIS','echem' UNION ALL
SELECT 'Bihag', 'MIS', 'CT' UNION ALL
SELECT 'Rajan', 'account','Marwadi' UNION ALL
SELECT 'Alka','account','tata' UNION ALL
SELECT 'Alpesh','Chemical','echem'
GO
DECLARE @Counter INT
SET @Counter =1
DECLARE @strName VARCHAR(200)
DECLARE @empCursor CURSOR
--declaring SCROLL cursor
--which will move first, last, forward and backward
SET @empCursor = CURSOR SCROLL FOR
SELECT Name FROM emps ORDER BY NAME
OPEN @empCursor
FETCH NEXT FROM @empCursor INTO @strName
--user of FETCH NEXT
WHILE (@@FETCH_STATUS = 0)
BEGIN
PRINT @strName + ' NEXT'
FETCH NEXT FROM @empCursor INTO @strName
SET @Counter = @Counter + 1
END
--user of FETCH PRIOR
WHILE (@Counter > 1)
BEGIN
FETCH PRIOR FROM @empCursor INTO @strName
PRINT @strName + ' PRIOR'
SET @Counter = @Counter - 1
END
--user of FETCH FIRST
BEGIN
FETCH FIRST FROM @empCursor INTO @strName
PRINT @strName +' FIRST'
END
--user of FETCH LAST
BEGIN
FETCH LAST FROM @empCursor INTO @strName
PRINT @strName +' LAST'
END
CLOSE @empCursor
DEALLOCATE @empCursor
GO
Note: this is very resource consuming cursor so think twice before use it.
Reference: Ritesh Shah/Rashmika Vaghela
